Math in Social Interactions!
Social Network Theory(SNT)
Have you ever wondered how Google, Facebook or Twitter became such a vast and large platform? Is there any mathematical concept behind it? Yes, there is: Social Network Theory! Networks have made it possible for Google, Facebook or Twitter like platforms to expand themselves. The theory explaining these social networks is known as Social Network Theory.
This blog post will give you an idea of what social network theory is and where it's used.
Social Network Theory is the part of Network Theory in Graph Theory. A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals, groups or organisation) and social interactions/relationships between actors. And the theory that explains these interactions/relationships is called social network theory(SNT). SNT tells us how networks influence behaviour. The graph of a social network consists of both dots/nodes and lines/edges where dots represent the actors and lines represent the relationship. We can create a graph of a social network by connecting these dots and lines - just like connect-the-dot puzzle!
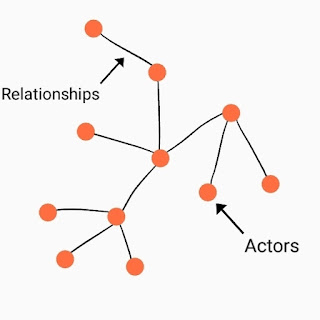 |
| Graphical representation of a network |
Main Aspects Of Social Network Theory
To get a better understanding of SNT we need to first understand the main aspects of SNT. There are mainly 3 aspects of SNT.
1) Network Environment & Actors
People or actors take actions based on their network environment. Network environment helps predict the existence of networks and its structure. It also helps us to know the kind of behaviour we can expect from the network. Actors with similar characteristics or interests tend to connect to each other and form a network. They might be alike in thoughts, theories or assumptions. This influences the network in a certain way.
e.g. Ami has a habit of reading books which might motivate her friends to develop the habit of reading. This forms a network of friends with a habit of reading.
 |
| Position of nodes in a network |
2) Position of Network
A person's position influences his/her behaviour. If a person's position is at the centre then he/she is the main actor in the network with access to many new information or ideas and receives a lot of attention. Actors at a bridging position connect individual actors in a network which enables links within a group and encourages collective actions. Those at the peripheral do not entirely behave the same like others in the network i.e. they are free from social norms of the community or group.
e.g. Ami is at the centre having main attraction. At the bridging position are her friends having the habit of reading, who might encourage their siblings or other friends to develop the habit of reading. Those who hesitate to develop the habit of reading are at a peripheral position that's almost outside the network.
3) Network's Structure
Networks have structure and it influences system's performance.
Entire network structure is composed of following factors :
- Homophily : Actors with more similarities stay together.
- Reciprocity : Actor’s connection with an individual in the network is mutual.
- Transitivity : Actors with similar view points tend to behave more alike than others in a group.
- Centralization : Actors who share more similarities with others will become central members of the network.
- Small - world Character : Actors within a network can share many attributes to other network groups.
In our example, the structure of the network is based on interest in reading books. Reading the same book together can increase bonding with each other(homophily & reciprocity). Friends who read a certain genre of books form a subgroup within the network(transitivity). People who read various genre of books are connected to many others in the network(centralization). Friends who have a habit of reading books might form relationships with friends who read blogs(small-world character).
Analysis of SNT
SNT can also be used for analysis. Data analysis carried out to understand social networks is called "Social Network Analysis(SNA)". SNA helps to evaluate these relations using visualisation, mathematical algorithms and computational tools. SNA gives an in-depth view of relationships in a network. What makes SNA different from other analysis is:
- Groups are not assumed to be societal building blocks.
- Studies usually focus on how interactions affect individuals and other relationships, versus discrete actors (individuals, organizations or states).
- Studies also focus on structure, the composition of interactions and how they affect societal norms, versus assuming that socialized norms determine behaviour.
Where can one use SNT?
SNT can be used in many areas such as organizational studies, art network- network of artists, communication studies, understanding community development, criminal networks- helps to find criminals, studies of language and linguistics, social media, advertising and many more.
SNT is mostly used by companies for advertising purposes. SNT helps them to understand the behaviour of their target customers. Their main goal of this study is to understand consumer behaviour and drive sales. For this purpose, the best way to get the required data for analysis is through social media.
Social Media is the best way for understanding social networks. Each day more than 55% of people are connecting and engaging in various topics via social networking sites. Their bond encourages them to change their behaviour and thoughts. With every like, subscribe and share, social network groups are being formed worldwide.
This is cool. Thank you
ReplyDeleteNice blog👍
ReplyDeleteVery informative!
ReplyDelete